During Meiosis the Cytokinesis That Follows Telophase Ii Results in
It is also used for cell reproduction. What occurs during telophase II and the process of cytokinesis that follows it.
What is the process in which homologues align gene by.

. It is initiated immediately after cytokinesis. This is called as diad of the cells. Duplicated chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell.
The primary function of mitosis is general growth and repair. The stage between two meiotic divisions is called interkinesis and it is short lived that follows Prophase II. Meiosis-II is known by another term ie homotypic division because in this division chromosome number remains same as produced in meiosis-I.
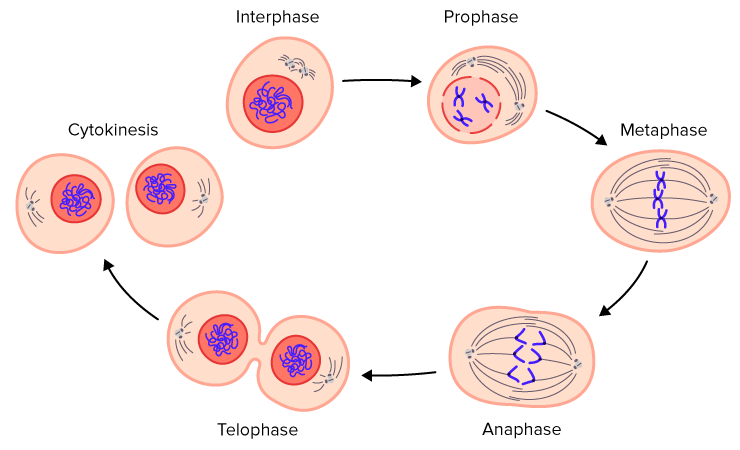
Four haploid cells are formed. Haploid and the chromosomes are each composed of a single daughter chromosome. MITOSIS MEIOSIS osmsitmitosis-and-meiosis Two processes of cell division MITOSIS Division of cell into two identical daughter cells Part of cell cycle Consists of prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Prophase Chromatin fibers condense Centrioles align chromosomes between centrosomes Metaphase Prometaphase.
It is initiated immediately after cytokinesis before chromosome gets elongated. During mitosis or meiosis sister chromatids are held together by proteins referred to as. Meiosis I begins with the interphase moving on through the stages of prophase I prometaphase metaphase I anaphase I and finally telophase I and cytokinesis and is a procedure in which homologous chromosomes become separated.
Following meiosis I cells enter a period of rest called interkinesis or prophase II. Cytokinesis occurs only in telophase during mitosis while it occurs in Telophase 1 and telophase 2 during meiosis. Sister chromatids are separated and move toward opposite poles.
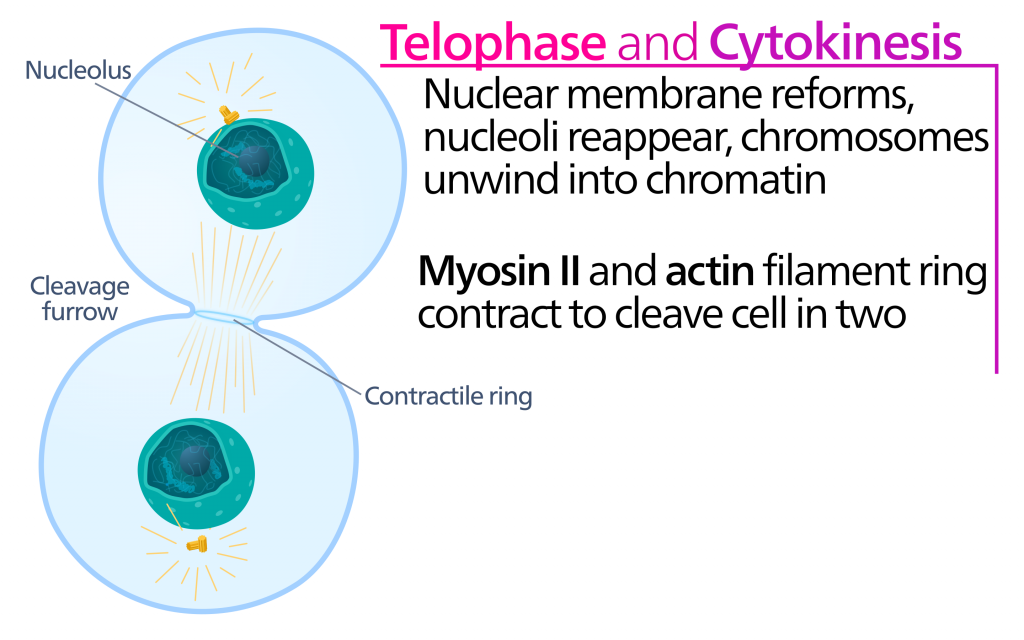
Meiosis always produces sex cells or gametes in the form of eggs or sperm. Chromatids are separated from each other during which of the following processes. During Telophase I nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappears and cytokinesis follows.
Cytokinesis - After the daughter cells split the two newly formed cells are haploid n. No DNA replication occurs during this stage. It is often known an equational division.
Meiosis-lf also resembles a normal mitotic division in contrast to meiosis-I because it distributes chromatids to daughter cells like mitosis. Nuclear membrane nucleolus disintegrate. In prophase II nuclear membrane disappears.
After telophase II of meiosis the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is. Homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange alleles. Process of division begins.
During both mitosis and meiosis II. Telophase I - Nuclear membrane reforms. Meiosis on the other hand aims to provide genetic diversity through sexual reproduction.

Solved During Meiosis The Cytokinesis That Follows Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment